First-aid Care: Poisonous Plants
Poison ivy, oak, and sumac can trigger painful skin reactions if not addressed quickly. Learn how to clean exposed skin, treat symptoms, and recognize when medical care is needed—all with standard first-aid supplies.
Working outdoors or in unfamiliar areas comes with the risk of brushing up against poisonous plants. Fast recognition and cleanup can help stop skin reactions before they start. This guide covers how to handle exposure safely, using practical first-aid methods to minimize discomfort and avoid serious allergic responses.
Being able to identify poisonous plants and avoid them helps reduce the risk of an allergic reaction. Poisonous plants contain toxins such as alkaloids, glycosides, resins, and tannins. About 90 percent of the U.S. population is allergic to urushiol sap oil in poison ivy, oak, and sumac.
Signs + Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of exposure to a poisonous plant vary depending on the type of plant, how the exposure occurred, and individual sensitivity. Symptoms of skin contact may include rash, swelling, blisters, and itchiness. Ingestion may cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Inhalation of smoke containing plant toxins may cause difficulty breathing, wheezing, coughing, and a sore throat.
First Aid
- For a suspected exposure:
- Clean skin with rubbing alcohol, skin cleanser, or soap and water
- Scrub under fingernails with a brush
- For a rash:
- Apply a wet compress, calamine lotion, or hydrocortisone cream (1%)
- Take an over-the-counter antihistamine as directed to help relieve itching; make sure it won’t make you drowsy
- Try to resist scratching; it can cause an infection
- Get immediate medical care for:
- Swelling and rash on the face or genitals
- Prior severe reactions to exposures
- Difficulty breathing
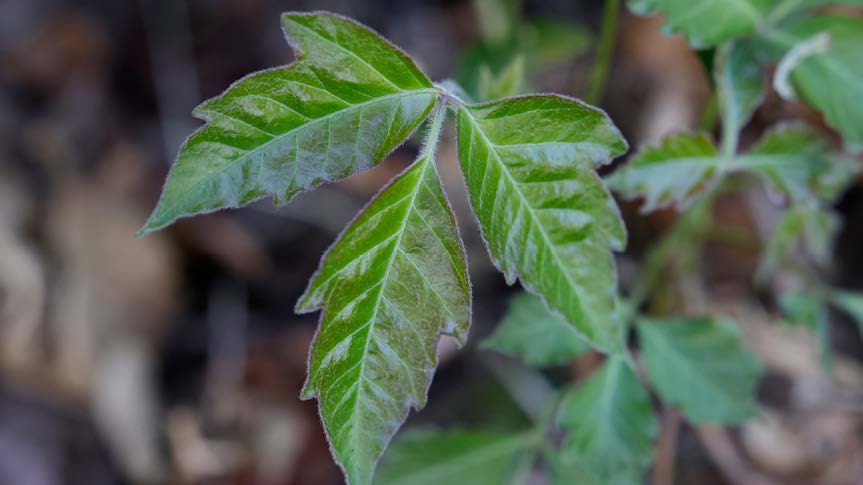

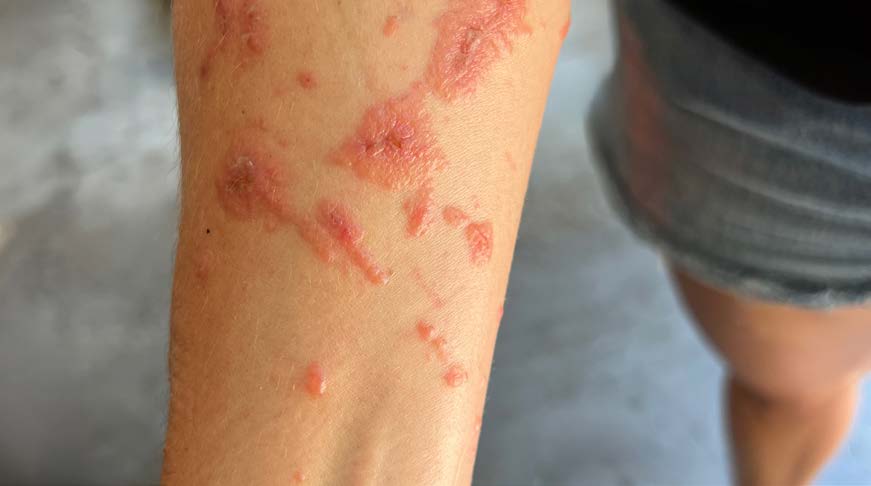
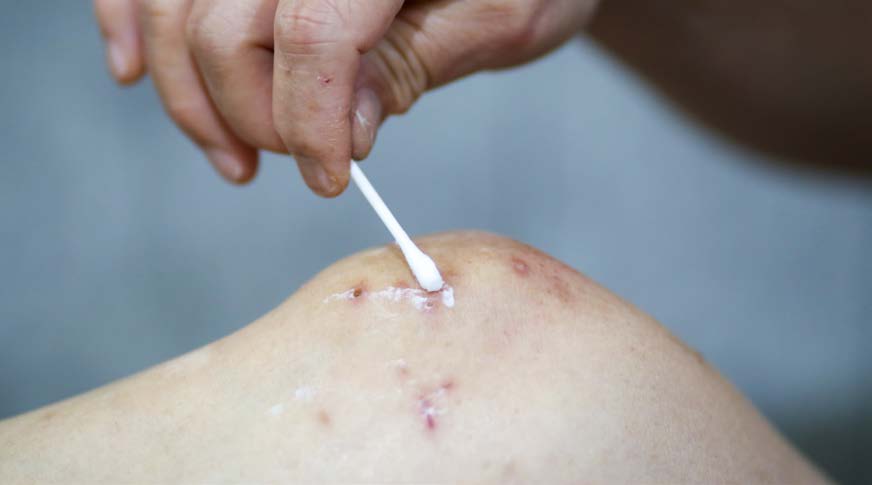
First-aid Supplies for Reactions to Poisonous Plants
WorkCare recommends keeping the following supplies on-hand in your first-aid kits:
- Skin cleanser
- Rubbing alcohol
- Cold packs
- Calamine lotion
- Hydrocortisone cream (1%)
- Non-prescription antihistamine
Note: Most reactions occur after coming into direct contact with a poisonous plant, getting toxins on clothing, or touching a pet that has been exposed.
Let’s Work Together
Ready to take your workforce health and safety to the next level?
Contact us today to learn how WorkCare can partner with you to create a healthier, safer, and more productive workplace.
