Use Body Mass Index, Waist Size to Measure Fat, Calculate Health Risks
Body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference are relatively reliable and affordable ways to measure body fat, identify health risks and establish weight-loss goals.
What is BMI?
Body Mass Index (BMI) is used as an indicator of obesity/overweight and risk for the development of diabetes, hypertension, coronary heart disease, osteoporosis, sleep apnea and other health conditions. BMI is calculated the same way for adults and children:
| Measurement Units | Formula and Calculation |
| Pounds and inches | Formula: [weight (lbs) / [height (in)]2 x 703 Calculate BMI by dividing weight in pounds by height in inches squared and multiplying by a conversion factor of 703. Example: Weight = 150 lbs, Height = 5’5” (65”) Calculation: [150 ÷ 65]2 x 703 = 24.96 |
| Kilograms and meters (or centimeters) | Formula: [weight (kg) / [height (m)]2 With the metric system, the formula for BMI is weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared. Divide height in centimeters by 100 to obtain height in meters. Example: Weight = 68 kg, Height = 165 cm (1.65 m) Calculation: [68 ÷ 1.65]2 = 24.98 |
For adults, a BMI of 25 is classified as overweight; over 30 is classified as obese. Although BMI does not measure body fat directly, it has been shown to correlate with direct measures of body fat using underwater weighing or dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA), a technique used to measure bone mineral density. Because BMI includes both muscle and fat, some individuals may have a high BMI but not a high percentage of body fat. For example, a professional athlete may be lean but have a high BMI because of increased muscularity.
Waist Circumference
The National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute recommends measuring waist circumference because abdominal fat is a predictor of risk for heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Health risks increase along with waist size greater than 35 inches for women and greater than 40 inches for men.
To measure your waist, stand, put a tape measure around your mid-section just above your hips and breathe out.
Classification of Overweight and Obesity by BMI, Waist Circumference and Associated Disease Risks
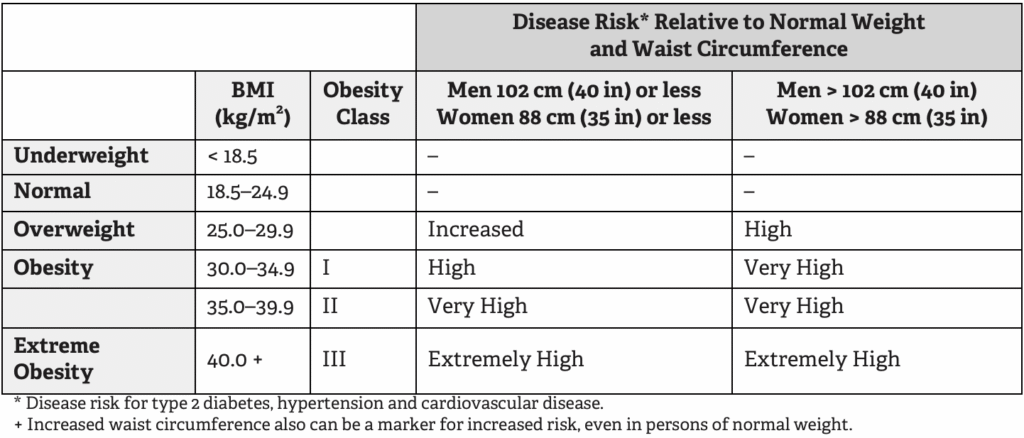
Other Factors
In addition to body fat, other factors that affect health risk include gender, ethnicity, age and lifestyle, including diet, exercise and smoking. For example, women tend to have more body fat than men and older adults tend to have more body fat than younger adults.
If you have questions or concerns about the appropriateness of your weight, contact WorkCare’s clinical team or discuss them with your personal health care provider.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: http://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/assessing/bmi/adult_bmi/index.html
- National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/educational/lose_wt/risk.htm
Let’s Work Together
Ready to take your workforce health and safety to the next level?
Contact us today to learn how WorkCare can partner with you to create a healthier, safer, and more productive workplace.
